
RBI Maintains Status Quo; Growth Stays Strong as Inflation Remains Benign
#
6th Feb, 2026
- 141 Views
NDNC disclaimer: I hereby authorize Bajaj Life Insurance Limited. to call me on the contact number made available by me on the website with a specific request to call back. I further declare that, irrespective of my contact number being registered on National Customer Preference Register (NCPR) or on National Do Not Call Registry (NDNC), any call made, SMS or WhatsApp sent in response to my request shall not be construed as an Unsolicited Commercial Communication even though the content of the call may be for the purposes of explaining various insurance products and services or solicitation and procurement of insurance business
Comments from Mr. Srinivas Rao Ravuri, Chief Investment Officer, Bajaj Life Insurance
Policy Decision: RBI Holds Rates, Maintains Neutral Stance
The Reserve Bank of India’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) kept the policy repo rate unchanged at 5.25% while reiterating its neutral stance. The unanimous decision reflected the MPC’s assessment that domestic macroeconomic conditions remain supportive even as global headwinds have become more challenging. Heightened geopolitical tensions, and cautious global monetary settings have created uncertainty, but India continues to maintain strong growth amid low inflation.
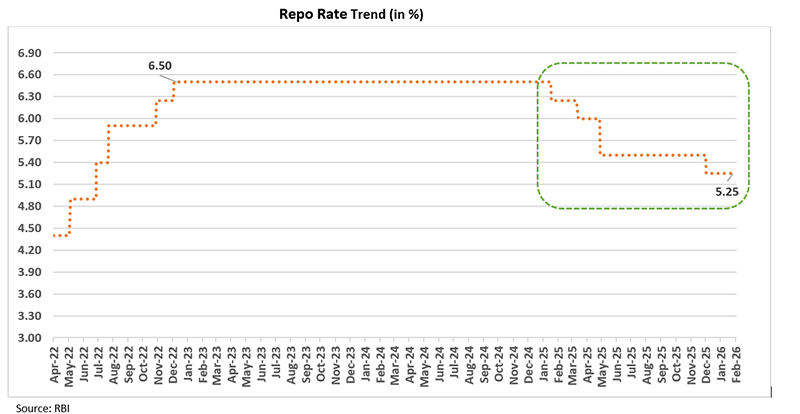
Growth Outlook: Domestic Momentum Remains Resilient
Economic activity remains robust, with India projected to grow at 7.4% in FY2025–26, supported by healthy consumption trends, strong fixed investment and an improving manufacturing and services sector. Both rural and urban demand remain steady, aided by favorable agricultural prospects and improving corporate performance. Investment activity is expected to strengthen further, driven by high-capacity utilization, accommodative financing conditions, and sustained government infrastructure spending. The RBI has revised its real GDP growth projections for Q1 and Q2 of FY2026–27 upwards to 6.9% and 7.0%, respectively, signaling confidence in continued momentum despite a fragile global backdrop.
Inflation: Benign Trends with Limited Upside Risks
Headline inflation remained below the tolerance band in November and December, though it edged up slightly due to a slower pace of food price deflation. The RBI now expects FY2025–26 inflation at 2.1%, with Q4 inflation at 3.2%. For Q1 and Q2 of FY2026–27, inflation is projected at 4.0% and 4.2%, respectively. The marginal upward revision is largely attributed to higher global precious metal prices, contributing an estimated 60–70 basis points. Meanwhile, underlying inflation pressures remain muted, supported by strong foodgrain stocks, favorable sowing conditions and stable input costs. Nonetheless, the RBI flagged potential risks from global food and energy volatility and geopolitical developments.
External Sector: Resilience Amid Global Uncertainty
India’s external sector remains stable despite a widening merchandise trade deficit driven by higher imports. Services exports and inward remittances continue to perform strongly, keeping the current account deficit contained and sustainable. India’s external buffers remain strong, with foreign exchange reserves at USD 723.8 billion, providing more than 11 months of import cover and ensuring resilience against global volatility.
Liquidity & Transmission: RBI Ensures Smooth Financial Conditions
Liquidity conditions stayed in surplus, averaging ₹ 70,000 crore, although the overall surplus moderated from earlier months. To maintain orderly financial conditions, the RBI conducted OMO purchases, long‑term forex buy/sell swaps and variable rate repo operations. Transmission has progressed well, with lending rates on fresh loans declining by 105 bps since the beginning of the easing cycle and term deposit rates also softening. The central bank reaffirmed its commitment to proactive liquidity management to accommodate fluctuations in government balances, currency demand and foreign exchange operations.
Financial Stability: Banking and NBFC Metrics Strengthen Further
India’s financial system remains strong, with scheduled commercial banks reporting robust capital adequacy, improved asset quality and stable profitability. Gross NPAs declined to 2.05%, while NBFCs continued to maintain comfortable capital buffers and healthier asset quality indicators. Credit growth accelerated to 13.1% year‑on‑year, supported by broad‑based lending across retail, MSME, services and industry segments, reflecting a deepening of credit availability across the economy.
Outlook & Market View: Balanced Tone with Support for Growth
The RBI maintained a balanced tone, noting comfort with the current growth‑inflation mix while remaining vigilant to global uncertainties and upcoming data releases, particularly the new GDP and CPI series. With growth inflation likely to normalize to RBI target, we believe RBI rate cut cycle is over, RBI is expected to maintained repo rate at current level for FY27. We expect the 10‑year G‑Sec yield to trade in the 6.60%–6.90% range and continue to prefer 3–5-year corporate bonds.
Annexure:
CRR – The share of a bank’s total deposits that must be kept with the RBI in cash.
Stance – It gives an indication to the future policy action.
SDF – The rate at which Banks lend to RBI without collateral.
MSF –The rate at which RBI lends (provides emergency liquidity) to Banks.

Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Facebook
Twitter
pintrest
instagram
Whatsapp
Linkedin
More